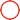
Also known as drawing. The process of drawing a preform rod by a drawing machine by melting it at high temperature and drawing it into an optical fiber with an outer diameter of 125μm. The quartz optical fiber drawing machine is as high as 10m or more. The preform rod is installed in the heating furnace at the top of the drawing machine. When the furnace temperature rises to about 2200℃, the viscosity of the tip of the rod becomes lower, and it gradually sags and becomes thinner by its own weight to become a bare optical fiber. The bare optical fiber passes through the laser diameter measuring monitor and then enters the coating and curing system. The coated optical fiber is then passed through the traction roller and then onto the reel. In the early 1990s, the international quartz optical fiber drawing speed was generally 300m/min, and the maximum could reach 1000m/min. The drawing process is shown in Figure 5. The laser diameter measurement and traction roller of the bare optical fiber are linked automatic control systems, which can ensure that the outer diameter of the bare optical fiber changes within a range. The entire drawing workshop needs to be ultra-clean and constant temperature, especially before the optical fiber is coated, to avoid any dust attachment to avoid affecting the strength of the optical fiber.
Optical fiber coating Although the optical fiber drawn from a preform rod of about 20mm into 125μm is thermally deformed, there are still microcracks on the surface of the bare optical fiber. If exposed to the atmosphere, the OH- in the atmosphere will expand the microcracks. Long-term exposure will cause the optical fiber to break, so the bare optical fiber must be coated quickly. Internationally, double coatings are used for UV curing. The first layer is a modified silicone resin with a small tensile modulus, high elasticity, low hydrogen evolution, and strong bonding performance to SiO2. The thickness is about 20μm to 30μm. It can improve the microbending resistance of the optical fiber and has good low-temperature characteristics. The second layer is a modified epoxy acrylic with extremely high tensile strength and elongation, which can provide sufficient strength protection and good surface performance for the optical fiber. The screening strength of the optical fiber coated in this way is above 5N, and its additional loss should be ≤0.05dB/km in the temperature range of -40 to +60℃.
All Products
-
Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
-
Indoor Fiber Optic Cable
-
ADSS Fiber Optic Cable
-
FTTH Drop Cable
-
Fiber Optic Patch Cord
-
Fiber Optic Accessories
-
CAT5E Ethernet Cable
-
CAT6 Ethernet Cable
-
CAT6A CAT7 CAT8 Cable
-
Network Patch Cord
-
CAT3 Telephone Cable
-
RG59 RG6 Coaxial Cable
-
KeyStone Jack FacePlate
-
RJ45 Connector
-
Network Patch Panel
Optical fiber production process
August 1, 2024