The production standards of network cables mainly involve two aspects: one is the physical properties of the network cables, such as the material, insulation layer, shielding performance of the cable, etc.; the other is the wiring standards of the network cables, that is, how to arrange the core wires in the cable to ensure the stability and efficiency of signal transmission. 12
Physical property standards:
Network cables usually use high-density polyethylene (HDPE) as the insulation layer to provide excellent near-end crosstalk performance and good mechanical properties.
The outer sheath material uses high-quality low-smoke halogen-free flame retardant materials with excellent flame retardant properties and low smoke characteristics to reduce the release of smoke and toxic gases during fire.
Wiring standards:
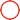
The International Organization for Standardization has specified two wire sequence standards - T568A and T568B. The main difference between them is the different core wire sequences.
The wiring sequence of T568A is: green and white, green, orange and white, blue, blue and white, orange, brown and white, brown; the wiring sequence of T568B is: orange and white, orange, green and white, blue, blue and white, green, brown and white, brown.
Although TIA recommends using T568A wiring, the two wiring methods have no effect on system performance. What is important is to maintain the consistency of the entire system.
In addition, the production of network cables must comply with relevant national or industry standards to ensure the safety and compatibility of the products. For example, "Polyethylene Network Cable" is an industry standard for network cable products, which stipulates the technical requirements and testing methods of network cables.
During the network cable construction process, certain construction requirements must be followed, such as inspection before cable laying, spacing requirements between cables and power cables, minimum bending radius, etc., to ensure the stable operation of the network system.